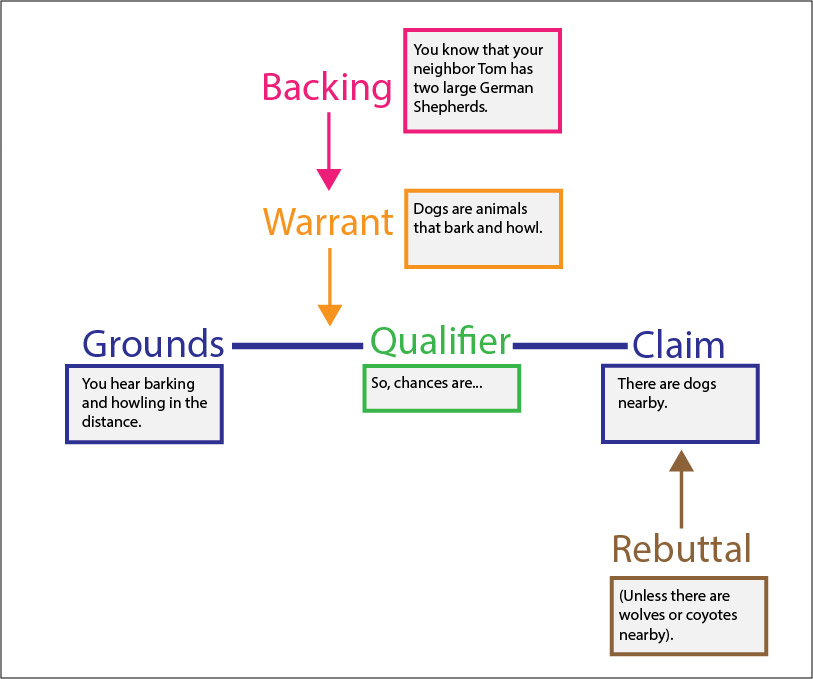
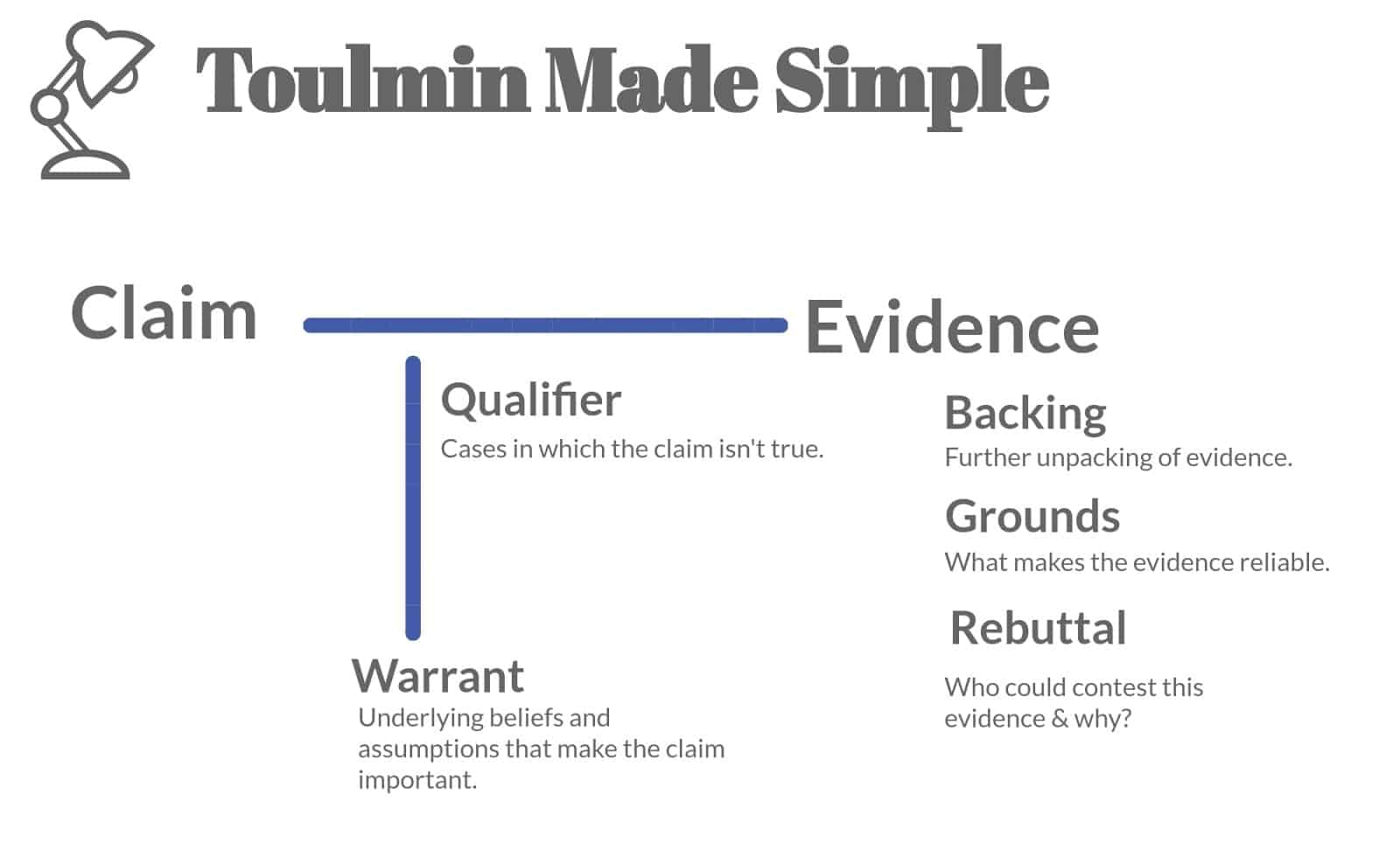
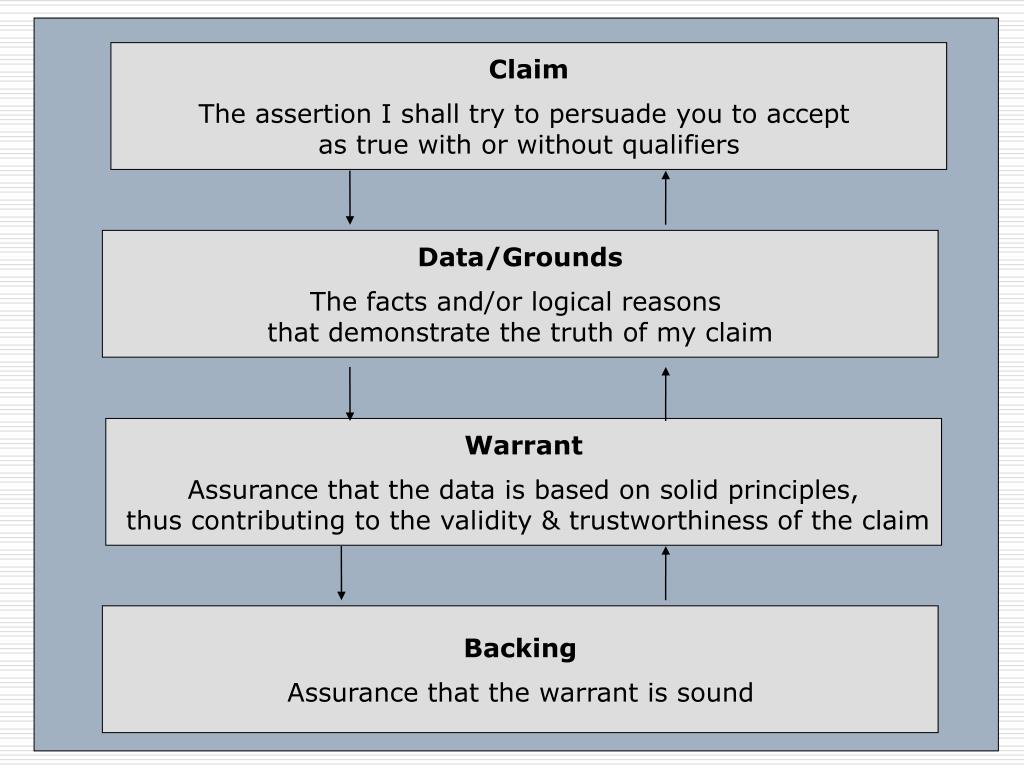
Toulmin Method Warrant - The exciting element of the warrant is. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. A claim is the assertion that. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument: The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal.
Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument: The exciting element of the warrant is. The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. A claim is the assertion that. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;.
A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that. The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. A claim is the assertion that. The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. The exciting element of the warrant is. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument:
Read The Claim. Then Explain The Warrant
The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. A claim is the assertion that. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument: In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
How To Organize a Paper The Toulmin Method The Visual Communication Guy
Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument: The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal.
PPT The Toulmin Model PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6134689
Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason. The exciting element of the warrant is. A claim is the assertion that. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why.
The Toulmin Argument Model Let's Get Writing!
A claim is the assertion that. In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts: The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The exciting element of the warrant is. A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that.
Toulmin Argument Purdue OWL® Purdue University
The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. A claim is the assertion that. The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument:
How to Build Strong Argumentation by Using the Toulmin Method
Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The exciting element of the warrant is. The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
PPT Teaching with the Toulmin Model PowerPoint Presentation, free
Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. A claim is the assertion that. The exciting element of the warrant is. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason.
The toulmin method of argument ppt download
A claim is the assertion that. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant. The exciting element of the warrant is. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; In toulmin’s method, every argument begins with three fundamental parts:
PPT The Toulmin Model of Argument PowerPoint Presentation, free
A claim is the assertion that. The exciting element of the warrant is. The warrant is often left unstated, it provides the logic of why. The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
PPT The toulmin method argument PowerPoint Presentation ID325159
The exciting element of the warrant is. The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. Toulmin identifies the three essential parts of any argument as the claim; The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument:
The Warrant Is Often Left Unstated, It Provides The Logic Of Why.
Stephen toulmin identified six elements of an argument: A claim is the assertion that. The data (also called grounds or evidence ), which support the claim;. The claim, the grounds, and the warrant.
In Toulmin’s Method, Every Argument Begins With Three Fundamental Parts:
The claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal. The exciting element of the warrant is. The warrant, the third fundamental part of toulmin’s model, serves to link the claim and the grounds. Warrants are chains of reasoning that connect the claim and evidence/reason.
Toulmin Identifies The Three Essential Parts Of Any Argument As The Claim;
A warrant is the principle, provision or chain of reasoning that.