Signs Of Brain Death After Cardiac Arrest - Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest The Lancet
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
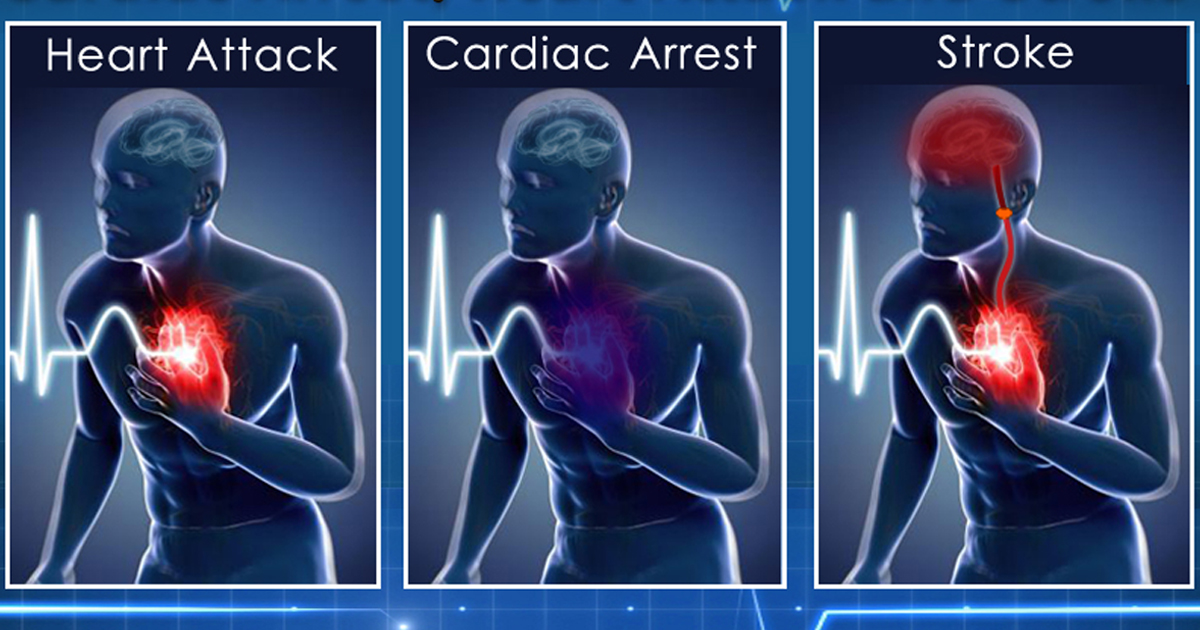
Learn the Key Differences Among, Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack and
In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
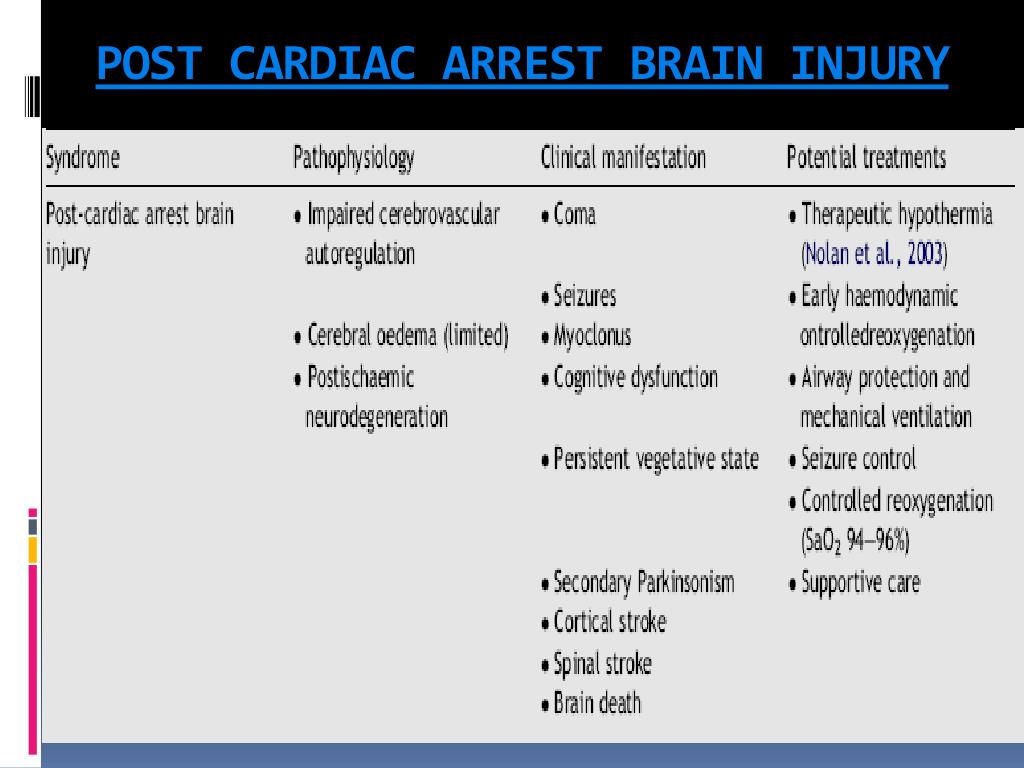
PPT Post cardiac arrest SYNDROME and post ROSC care PowerPoint
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
PPT …surprise at recovery PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
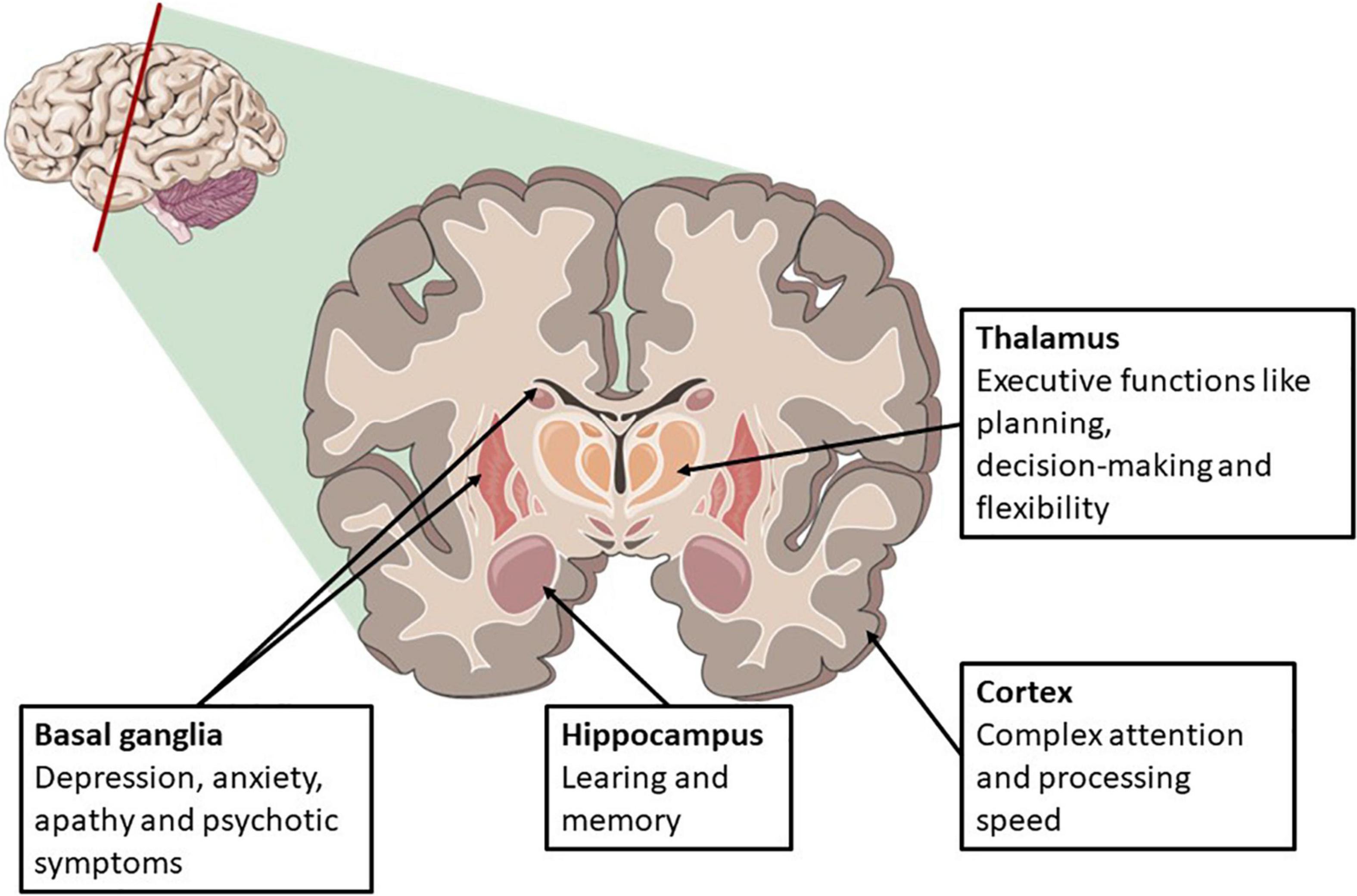
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
PPT Post Cardiac Arrest Patient in the ICU PowerPoint Presentation
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
Patient . After cardiac arrest, a request is submitted to rule out
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid.
PPT Post cardiac arrest SYNDROME and post ROSC care PowerPoint
In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
During a cardiac arrest there are two stages of brain injury https
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Brain Injury After Resuscitation, A Common Sequela Following Cardiac Arrest, Ranges In Severity From Mild Impairment To Devastating.
In approximately 5% of patients, cardiac arrest stems from a primary structural brain lesion such as aneurysmal subarachnoid. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.