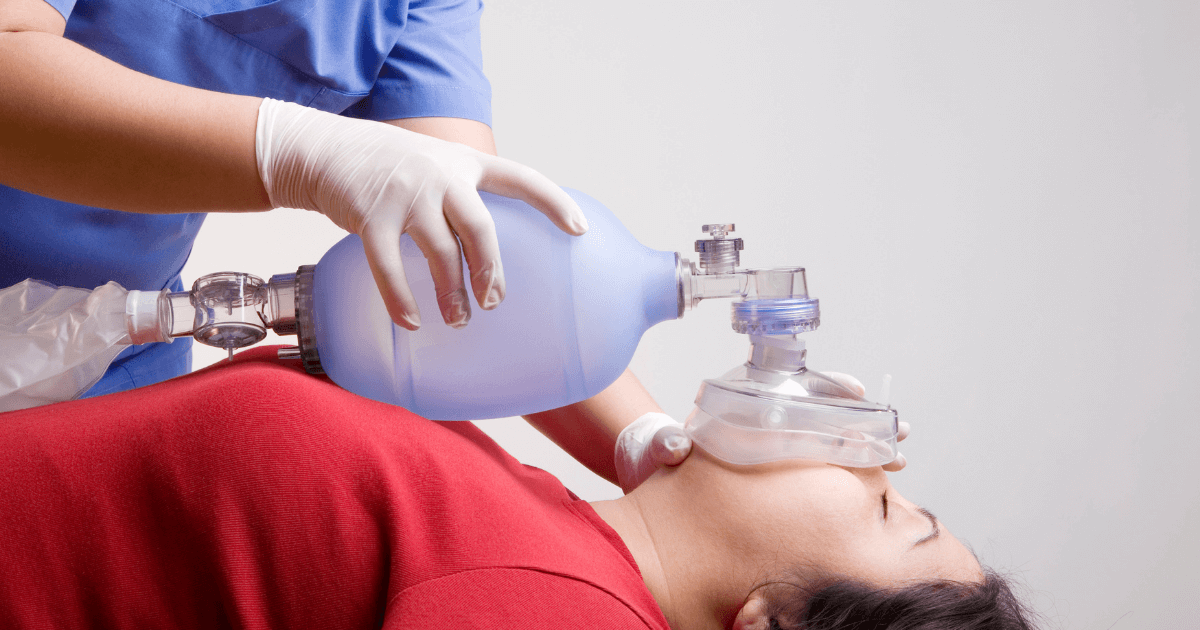
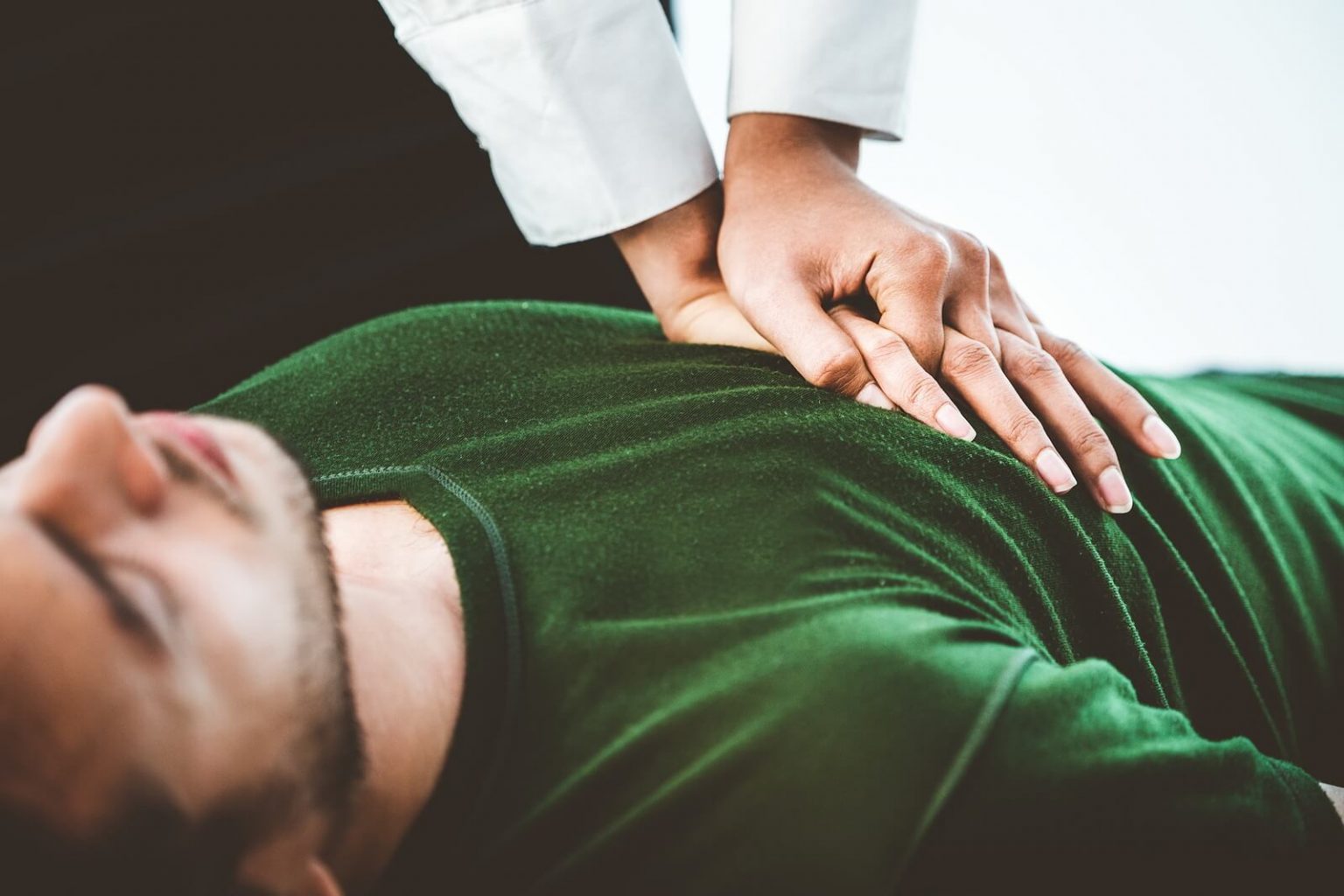
Respiratory Arrest Cpr - Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest. Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation ,respiratory arrest ,cardiac arrest
When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest. Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and.
Chapter 6 Respiratory Arrest (with pulse) American CPR Care
When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest. Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and.
Recognizing and Treating Respiratory Arrest
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
All You Need To Know About Respiratory Arrest Definition, Causes, And
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
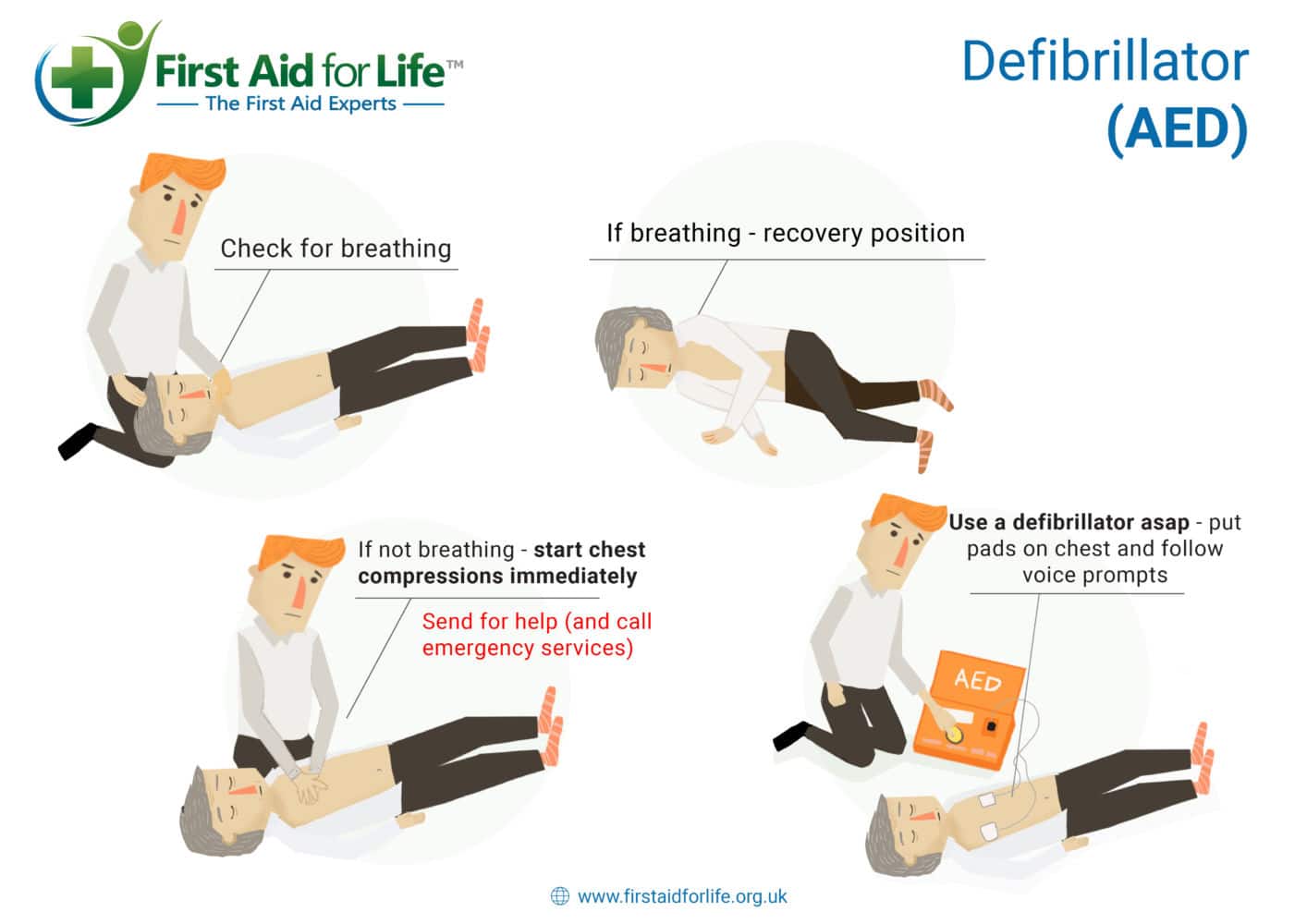
CPR Cardio, Pulmonary Resuscitation First Aid for Life
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
First Aid Illustration Resuscitation (Cpr), Cardiac Arrest Or
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
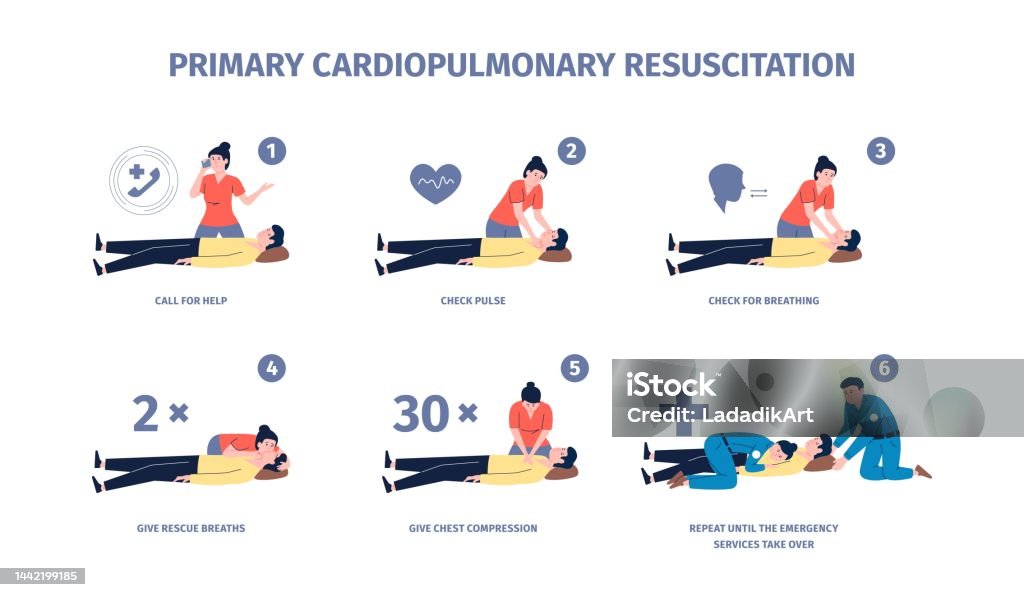
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Cpr Reanimation And First Aid Procedures
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
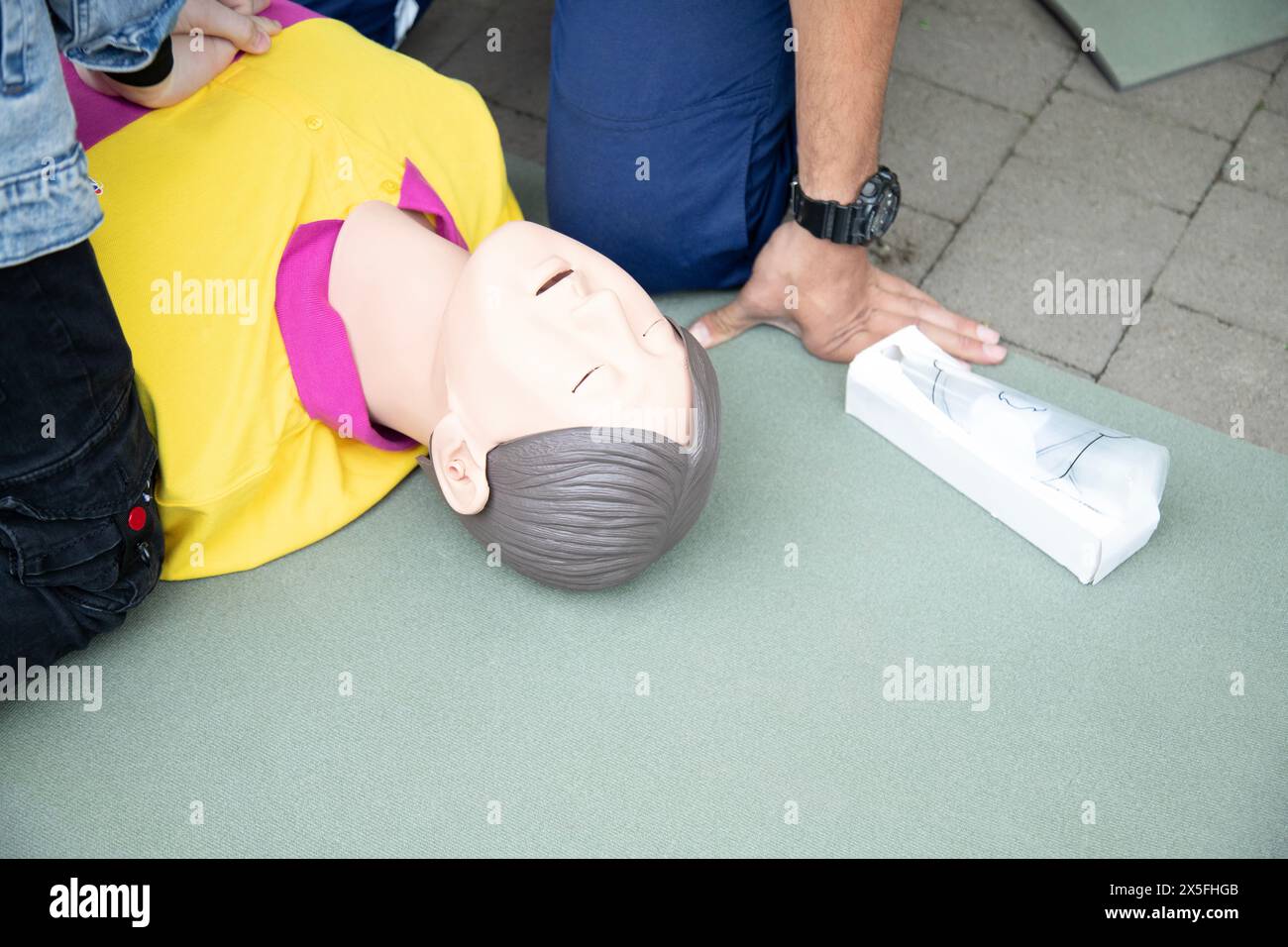
Do you do CPR for respiratory arrest? SureFire CPR
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
Differences Between Respiratory and Cardiac Arrest
When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest. Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and.
How to Do CPR Steps for Adults, Children, Babies
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and. When a patient goes into respiratory arrest, they are not getting oxygen to their vital organs and may suffer brain damage or cardiac arrest.
When A Patient Goes Into Respiratory Arrest, They Are Not Getting Oxygen To Their Vital Organs And May Suffer Brain Damage Or Cardiac Arrest.
Recognizing respiratory arrest, performing initial steps, opening the airway, checking for breathing and pulse, giving rescue breaths, and.



/adult-resuscitation-136811270-5a244663845b340036078f78.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-do-cpr-1298446-4a04444fabe0467aa9194a9161e5cdb2.png)