Myoclonic Jerking After Cardiac Arrest - Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is.
Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult.
Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from.
Myoclonic Jerk
Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic).
MYOCLONIC JERKS secondary to HYPOXIC BRAIN INJURY YouTube
Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after.
What is Myoclonus?, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & More
Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Although myoclonus less than.
Myoclonic Jerks Neurology Videos, Medical Videos YouTube
Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of.
The Key to Survival Dr Tong WL Associate Consultant ppt download
Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused.
Myoclonic Seizures Insights, Triggers, and Coping Strategies
Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks).
Diagnosis and management of seizures and myoclonus after cardiac arrest
Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of.
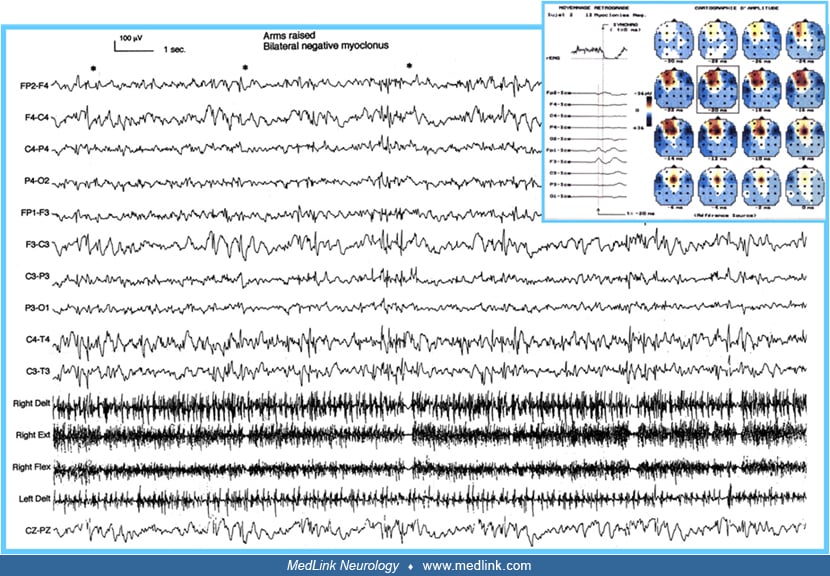
Myoclonic seizures MedLink Neurology
Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there.
Myoclonic Jerk
Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle.
MYOCLONIC JERKS YouTube
Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from. Accurate prediction of neurological outcome in survivors of cardiac arrest may be difficult. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks).
Accurate Prediction Of Neurological Outcome In Survivors Of Cardiac Arrest May Be Difficult.
Myoclonus, status myoclonus, and (electrographic) status epilepticus are signs of severe brain injury in comatose patients after. Myoclonic seizures (twitches or jerks) are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or by muscle relaxation,. Although myoclonus less than or equal to 72 hours after cardiac arrest (ca) is often viewed as a single entity, there is. Myoclonus, the brief involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles, occurs in about 20% of patients resuscitated from.