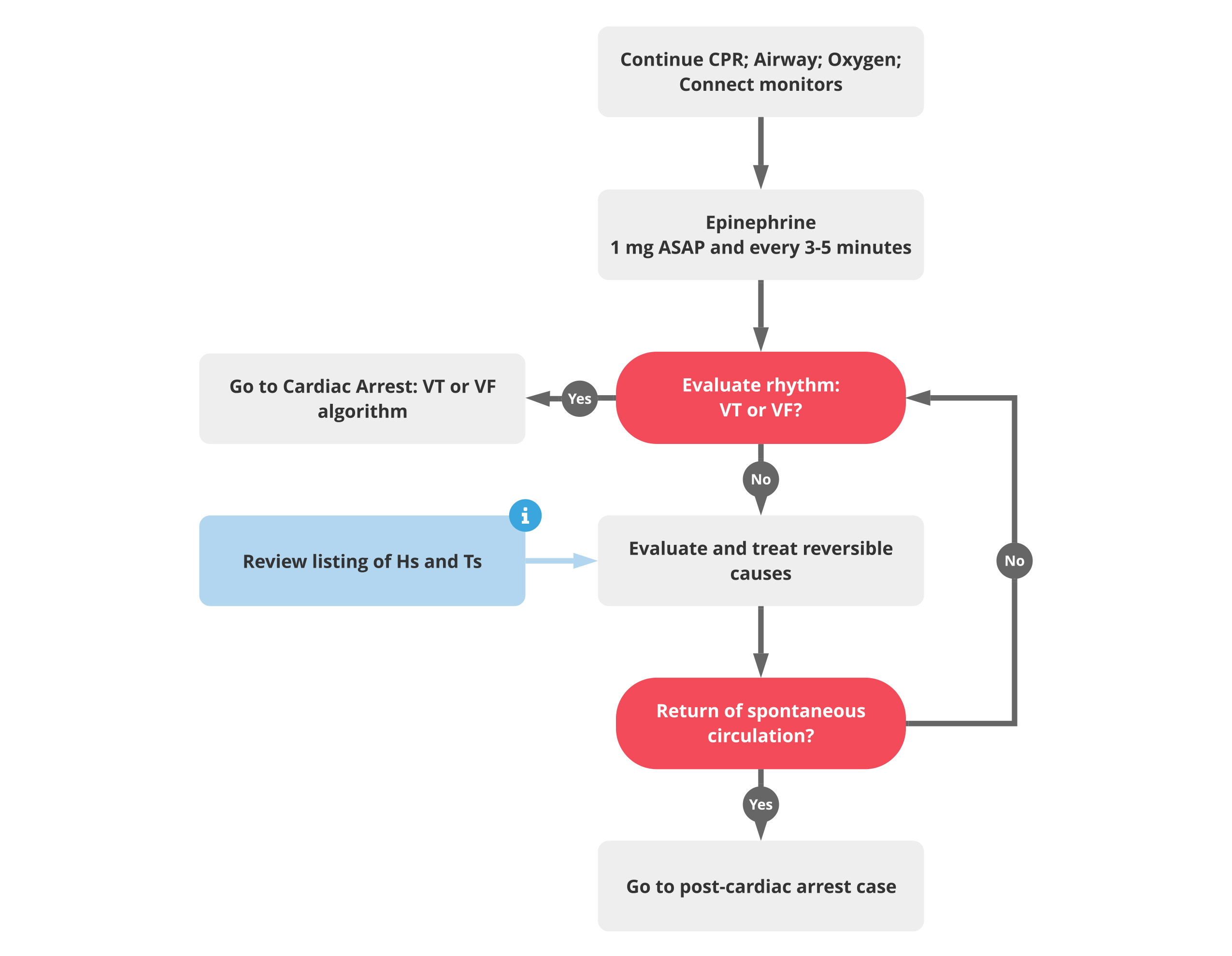
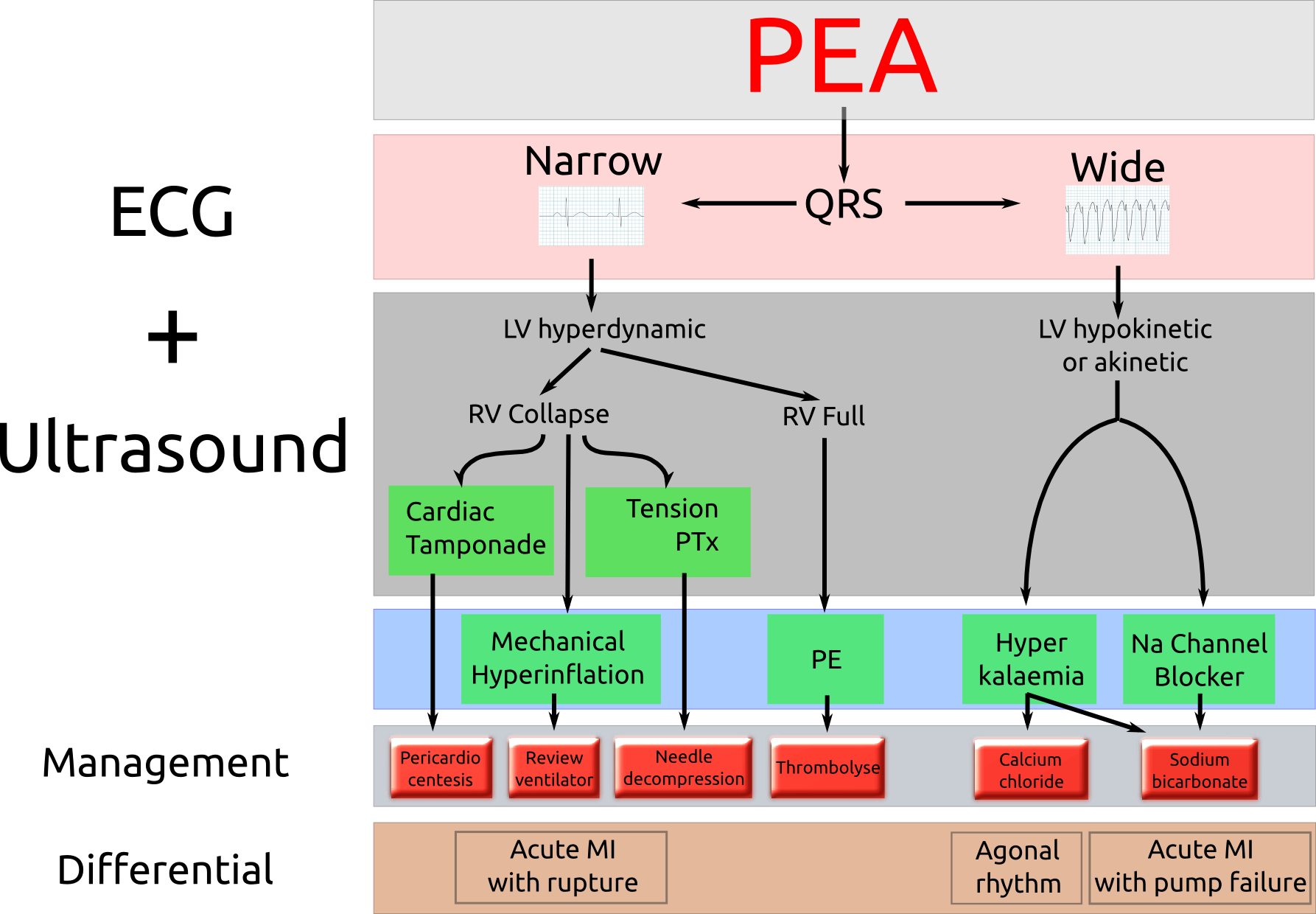
Cardiac Arrest With Pea - For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after.
Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after.
Asystole ACLS Protocol Advanced Cardiac Life Support
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to.
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Asystole/ PEA
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to.
Beyond ACLS A New Pulseless Electrical Activity Algorithm REBEL EM
For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after.
What is an AED & Why is it Important? A Compressive Guide
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to.
Cardiac Arrest (Asystole/ PEA) 2020 AHA Guidelines
Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after.
PEA and it's ACLS algorithm
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
Novel Management of PEA Arrest (Calgary EM Journal Club) SOCMOB Blog
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
Management of PEA in need of resuscitation? EMOttawa Blog
Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
Cardiac Arrest (Asystole/ PEA) 2020 AHA Guidelines
Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
PEA (pulseless electrical activity) ใน cardiac arrest, คือภาวะที่คลื่น
Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to. Pea, pulseless electrical activity is defined as any organized rhythm without a palpable pulse and is the most common rhythm present after. For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest.
Pea, Pulseless Electrical Activity Is Defined As Any Organized Rhythm Without A Palpable Pulse And Is The Most Common Rhythm Present After.
For adult patients who have no pulse and an organized cardiac rhythm (indicative of pulseless electrical activity), the acls cardiac arrest. Perform noninvasive technologies such as bioimpedance and bioreactance in experimental cardiac arrest and pea models to.