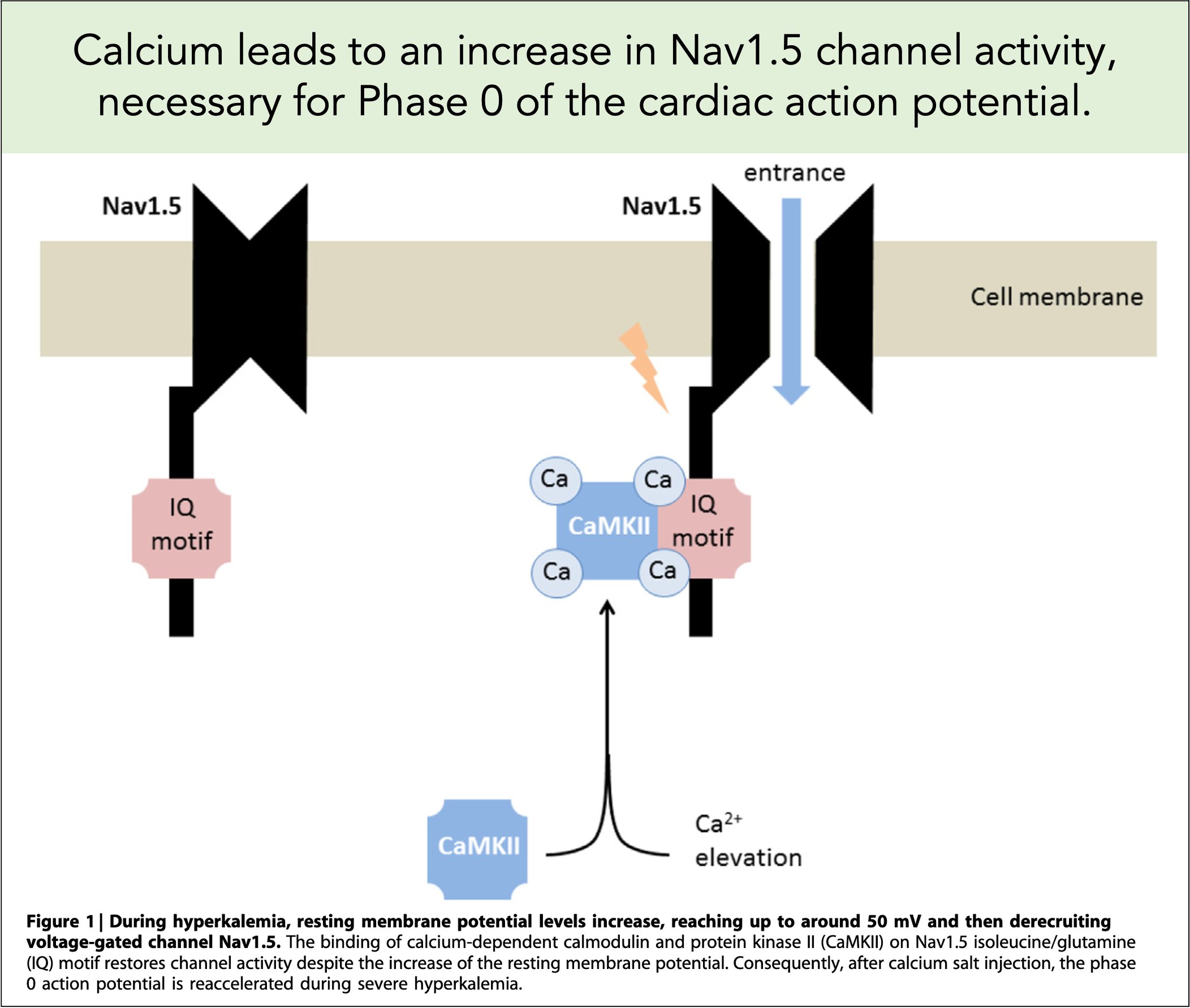
Calcium Chloride In Cardiac Arrest - Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit.
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit.
Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients.
Calcium in OutofHospital Cardiac Arrest NAEMSP
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not.
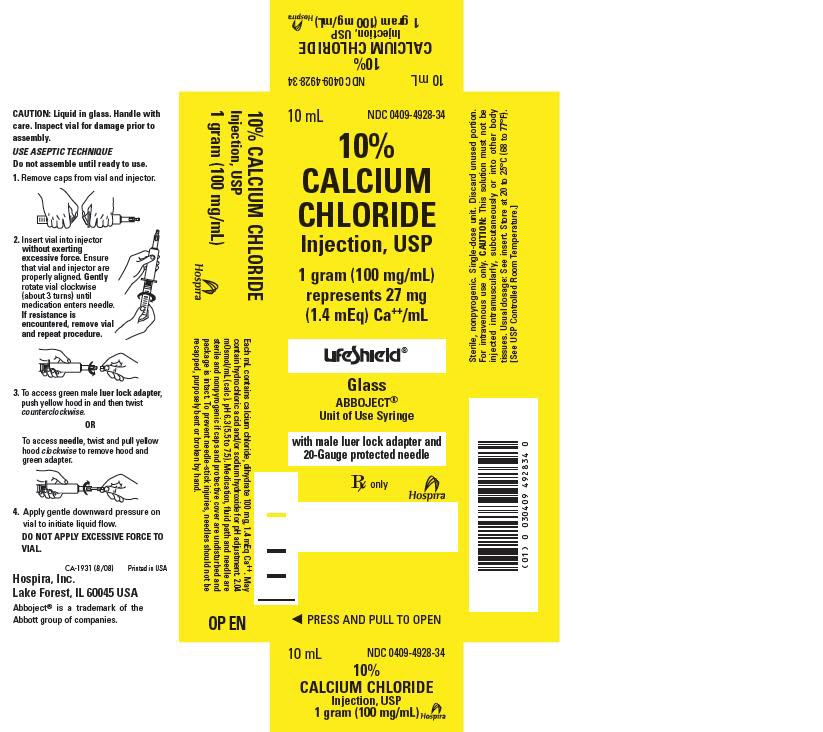
Calcium Chloride Injection Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not.
Calcium and Cardiac Rhythms Circulation Research
The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or.
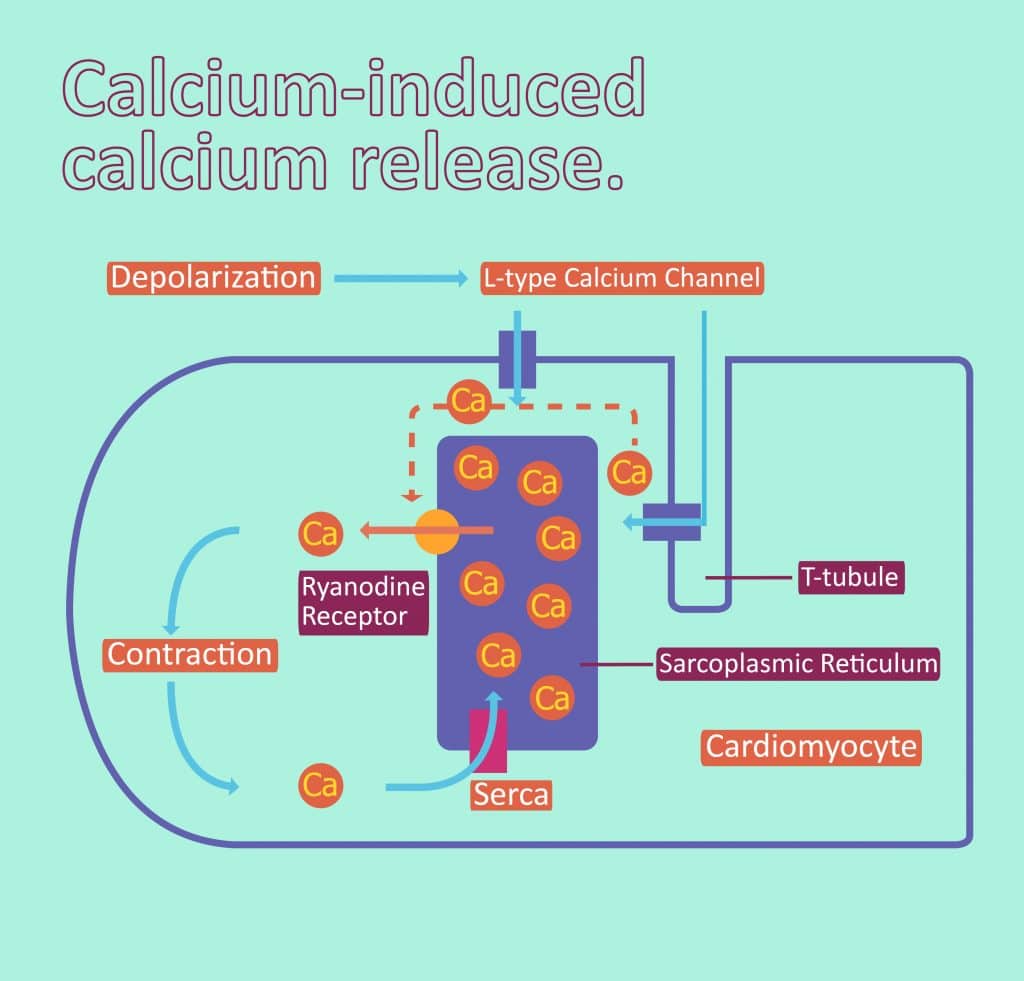
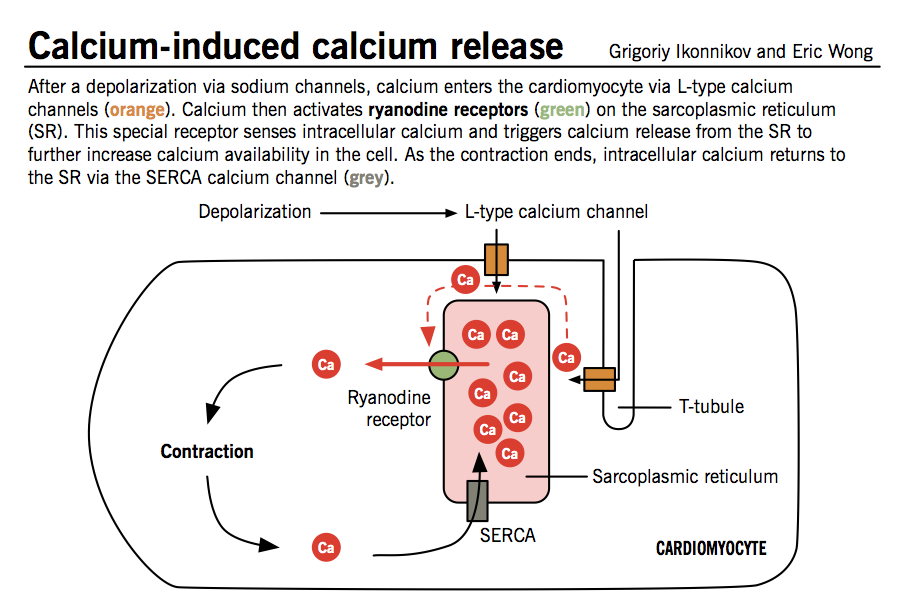
Contraction of Cardiac Muscle Pathway of Contraction TeachMePhysiology
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or.
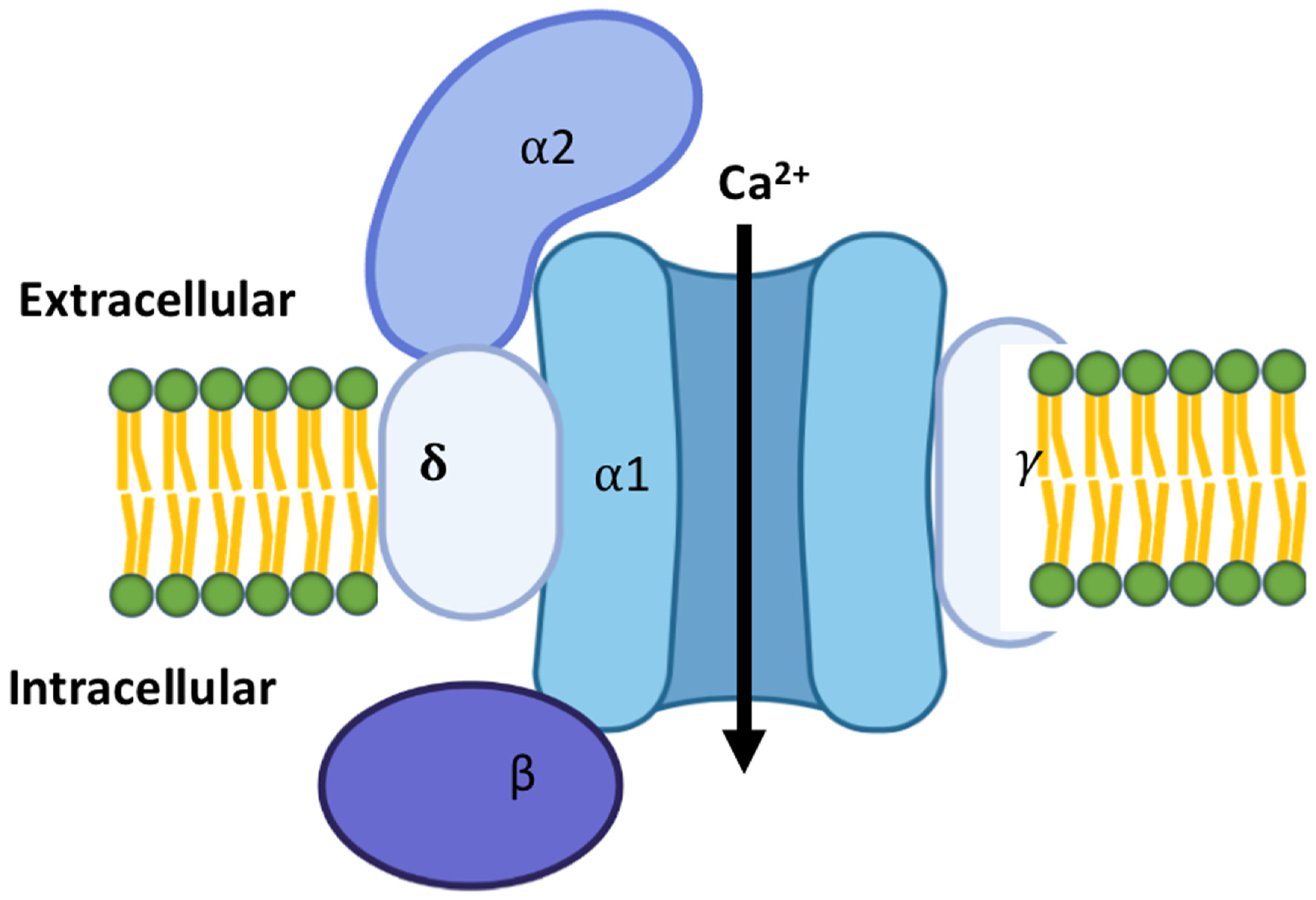
Cells Free FullText Calcium Channels in the Heart Disease States
The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or.
Part 12 Cardiac Arrest in Special Situations Circulation
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not.
Libération du calcium induite par le calcium — Wikipédia
Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not.
Calcium Administration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or.
Calcium and Cardiac Rhythms Circulation Research
The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of cardiac arrest patients. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or.
Tony Breu on Twitter "1/17 How does calcium "stabilize the cardiac
Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit. Calcium administration during cardiac arrest has been shown to have variable results on the outcome of.
Calcium Administration During Cardiac Arrest Has Been Shown To Have Variable Results On The Outcome Of Cardiac Arrest Patients.
Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The use of intravenous calcium chloride as a routine intervention in out of hospital cardiac arrest is not associated with benefit.