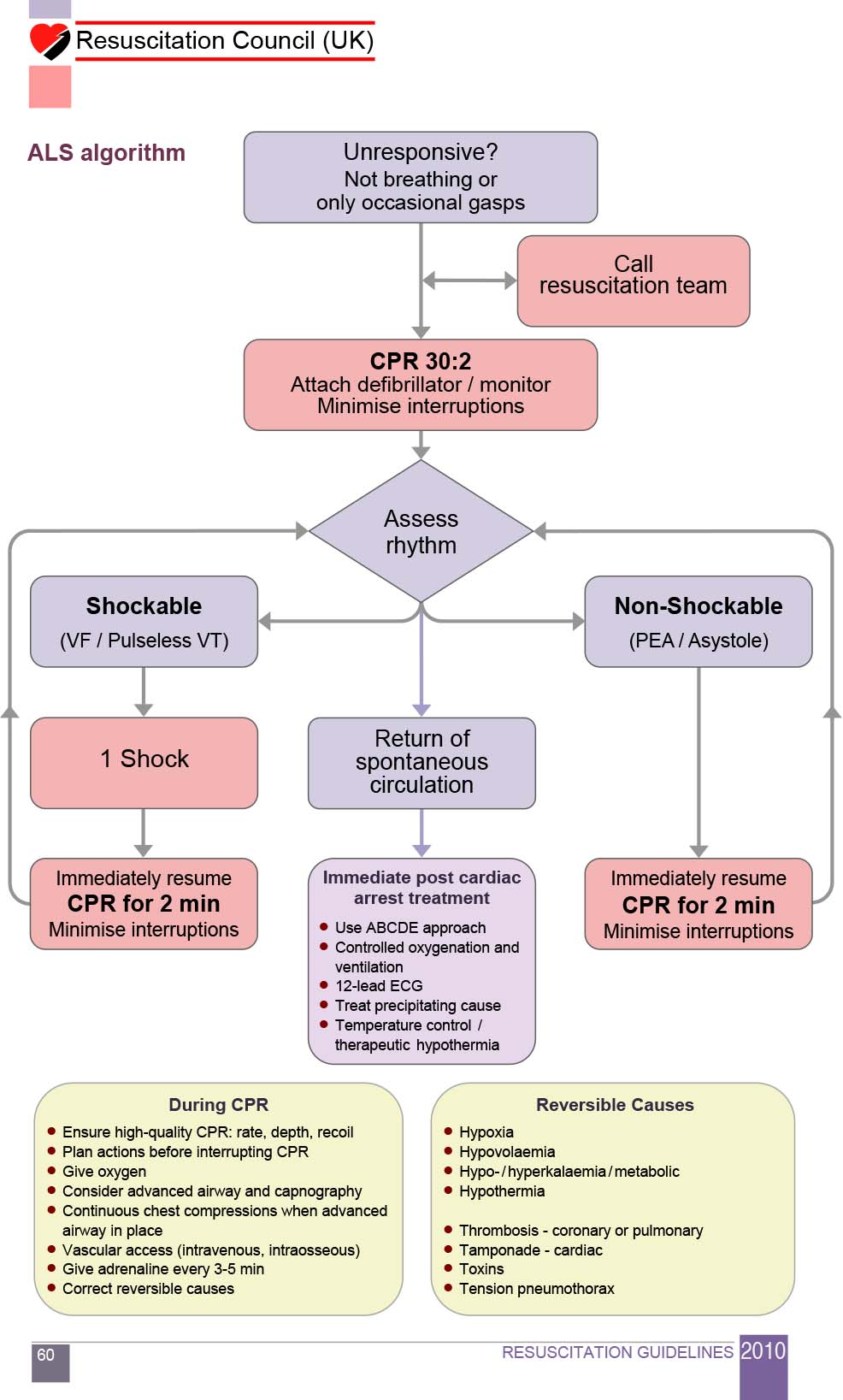
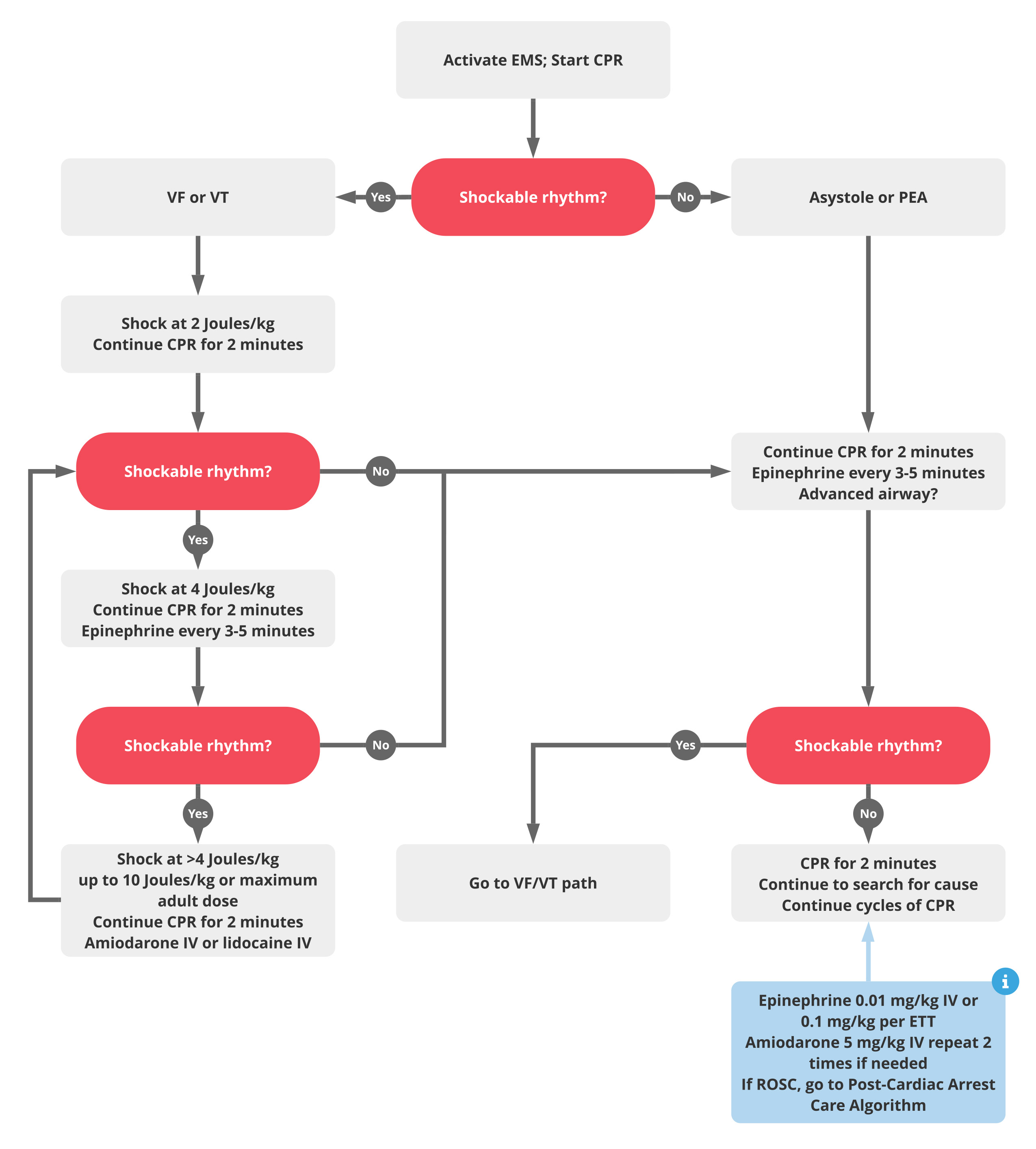
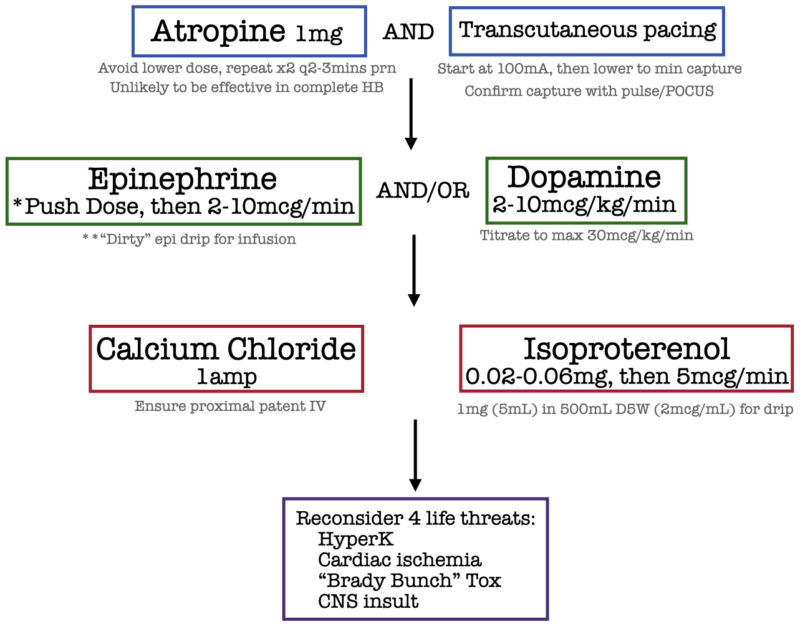
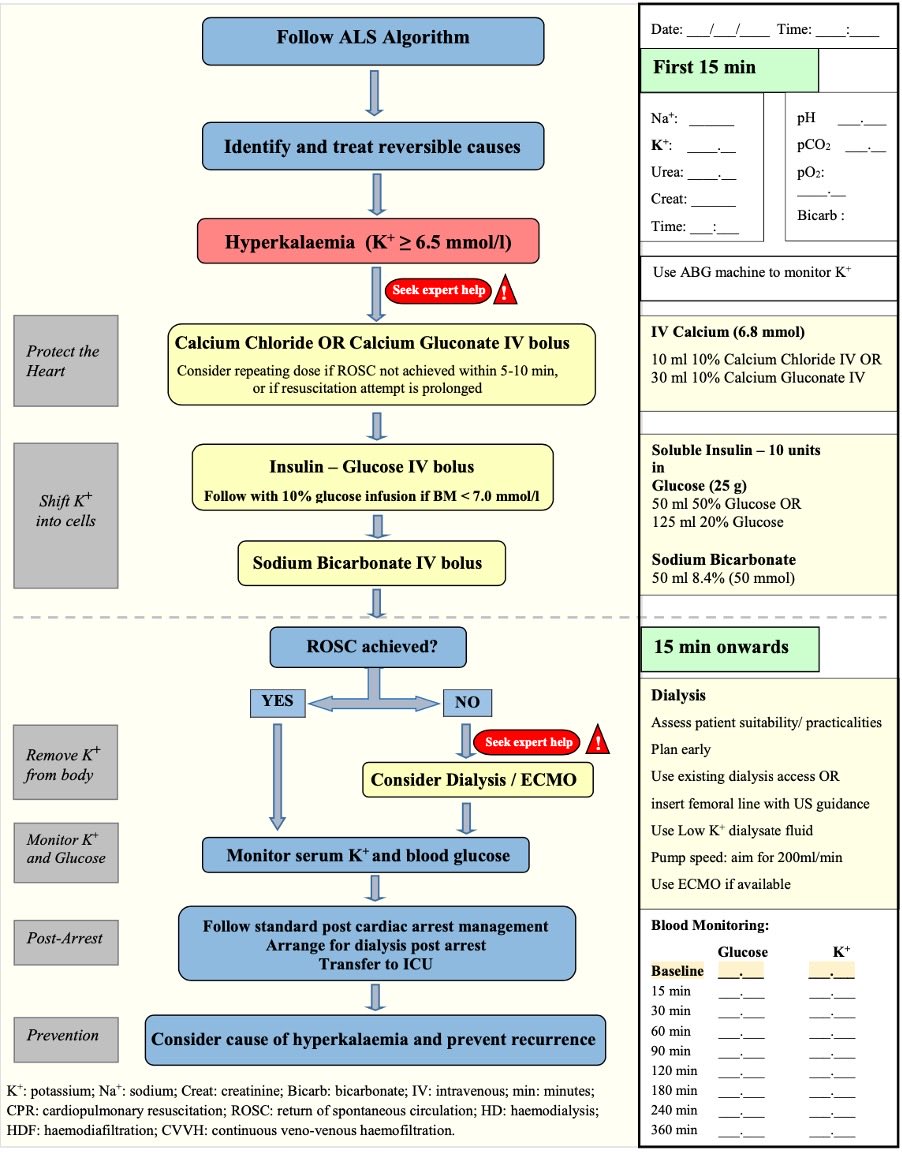
Calcium Chloride Cardiac Arrest - Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not.
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not.
Cardiac Arrest Oxford Medical Education
The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.
ACLS Algorithms You Need To Know
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.
A Standardized and Comprehensive Approach to the Management of
Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not.
PALS Certification Pediatric Advanced Life Support
The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to.
Treatment of Bradycardia and Bradydysrhythmias Emergency Medicine Cases
The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.
Treatment of Bradycardia and Bradydysrhythmias Emergency Medicine Cases
Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to.
DailyMed CALCIUM CHLORIDE injection, solution
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not.
Calcium in OutofHospital Cardiac Arrest NAEMSP
The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to.
Jamie Willows on Twitter "1/ As you can imagine the evidence base for
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one. The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not.
Part 12 Cardiac Arrest in Special Situations Circulation
The randomised controlled and observational studies showed that routine calcium administration during cardiac arrest did not. This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.
The Randomised Controlled And Observational Studies Showed That Routine Calcium Administration During Cardiac Arrest Did Not.
This topic highlights the results of the literature review on calcium therapy during cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation according to. Our results show that calcium administration during cardiac arrest was associated with no benefit (rr > 1.00) for rosc or survival at one.