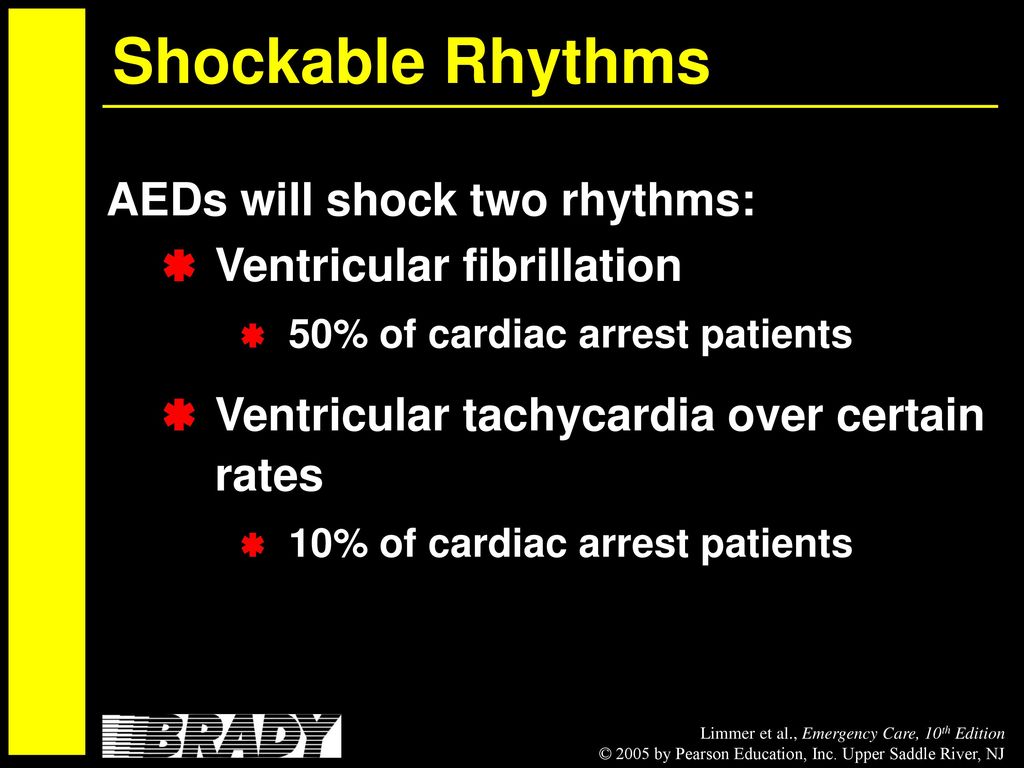
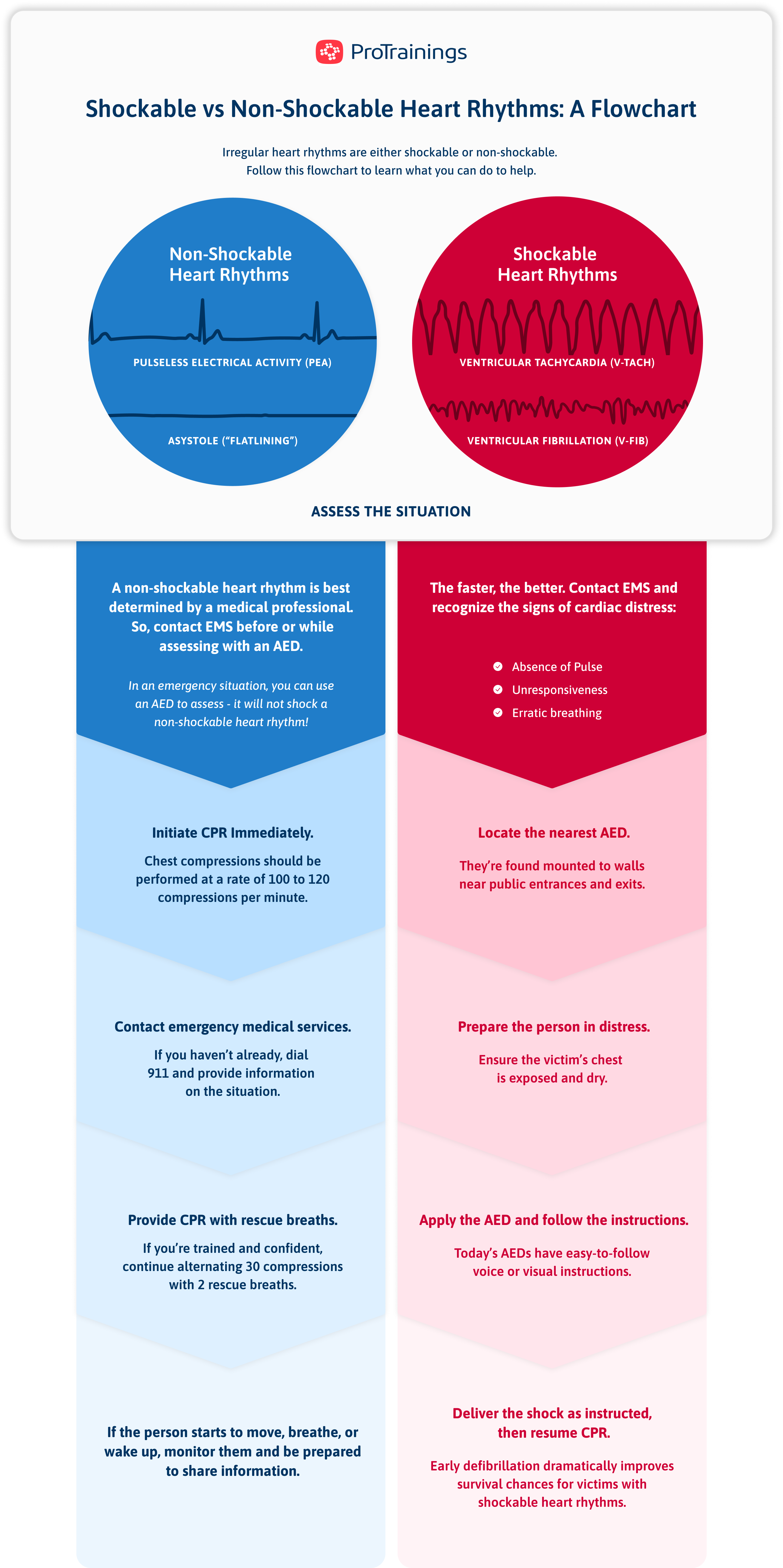
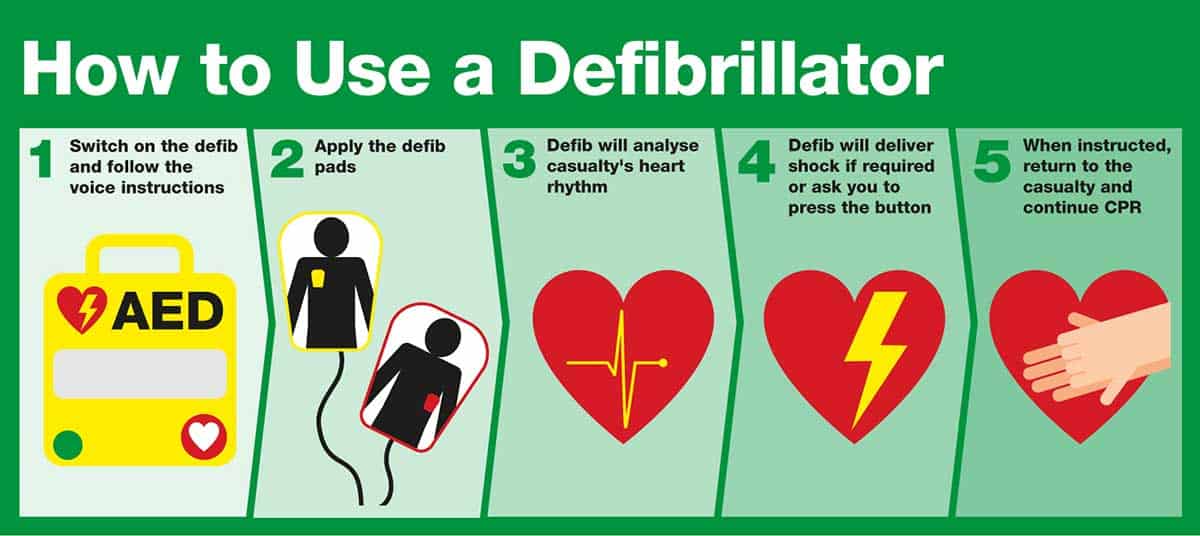
All Cardiac Arrest Situations Are Shockable By An Aed. - Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2% of public arrests. Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can.
Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2% of public arrests. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed;
Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2% of public arrests. An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest.
CHAPTER 17 Cardiac Emergencies. ppt download
Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; However, the number of patients who have.
Signs of Cardiac Arrest and How to Save a Life with an AED and CPR
An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by.
AED Shockable Rhythms Detecting 2 or 3 Shockable Arrhythmias
An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Cpr's.
Understanding NonShockable vs. Shockable Heart Rhythms
Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Some cases involve asystole (flatline).
Understanding Shockable vs. NonShockable Heart Rhythms
However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2% of public arrests. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. Some cases involve asystole.
An AED can ensure ‘current’ in your heart if it is ‘under attack
Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. However, the number of.
What to Know About Shockable vs. NonShockable Heart Rhythms ProTrainings
Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2% of public arrests. An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable.
Shockable vs. Non Shockable Heart Rhythms Avive AED
Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. However, the number of patients who have an aed applied by a bystander remains low, occurring after only 10.2%.
Workplace automated external defibrillator (AED) cardiac arrest
Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished. Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Some cases involve asystole.
How and when to use an AED during cardiac arrest The Washington Post
An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Cpr's primary function is to circulate blood until the heart can. Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished..
However, The Number Of Patients Who Have An Aed Applied By A Bystander Remains Low, Occurring After Only 10.2% Of Public Arrests.
An aed saves lives by delivering an electric shock that resets the heart’s rhythm during sudden cardiac arrest. Not all cardiac arrest situations are caused by shockable rhythms. Some cases involve asystole (flatline) or pulseless electrical activity (pea),. Aeds detect ‘shock able’ heart rhythms, typically ventricular fibrillation, associated with sudden cardiac arrests.
Cpr's Primary Function Is To Circulate Blood Until The Heart Can.
Not all cardiac arrest situations are shockable by an aed; Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like all cardiac arrests situations are shockable by an aed, what is accomplished.